Key Features
- Eye strain, also known as asthenopia, indicates overworked eyes and is not a disease in itself.
- One of the leading causes is prolonged exposure to digital screens, emitting harmful blue light.
- Working in inadequate lighting or reading for extended periods also contributes to eye strain.
- Symptoms like blurred vision, headaches, and sensitivity to light are common indicators.
- Typically, the discomfort from eye strain subsides after a few hours once the eyes are rested.
- Persistent symptoms may point to underlying vision issues that need addressing.
- Adopting habits like the 20-20-20 Rule—taking a break every 20 minutes to focus on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds—can help in prevention.
- Ensuring regular eye check-ups, using proper lighting, and optimizing screen usage are crucial for long-term eye health.
What is Eye Strain?

Eye strain, medically known as asthenopia, is a condition characterized by discomfort in and around the eyes. This discomfort often results from prolonged use of digital devices, reading, or performing any visual task that requires intense focus for extended periods. It’s essential to recognize that eye strain is a symptom, not a disease. It’s a signal from our body telling us that our eyes are overworked and need a break.
How Long Does Eye Strain Last?
The duration of eye strain largely depends on its cause and how soon you address it. For most people, symptoms of it will subside after a few hours once they give their eyes a proper break.
However, if you continue with the same habits that caused it in the first place, the discomfort will likely return. For instance, if you spend another long day in front of the computer without breaks, you’re setting yourself up for recurrent episodes of strain.
In cases where this strain results from uncorrected vision issues, the discomfort will persist until the underlying problem is addressed, often with corrective lenses or other treatments.
Causes of Eye Strain

Following are some causes of Eye Strain:
Digital Device Use
The most common cause in recent times is staring at screens for hours, be it your smartphone, computer, or television, which can lead to eye strain. The blue light emitted by these devices, combined with the constant focus on close-up text and images, stresses our eyes.
Improper Lighting
Working in dimly lit areas or under harsh fluorescent lights can strain our eyes. It’s crucial to have ambient lighting that’s neither too dim nor too glaring.
Reading for Extended Periods

Just like digital device use, prolonged reading without breaks can fatigue the eyes, especially if the text is too small or the lighting isn’t ideal.
Uncorrected Vision Problems
Suppose you have refractive errors like myopia (short-sightedness), hyperopia (long-sightedness), or astigmatism, and they aren’t corrected with proper eyewear. In that case, you are more likely to experience eye strain.
Inadequate Eye Rest
Our eyes, like any other muscle in the body, need rest. If you continuously engage in visually intense activities without taking breaks, your eyes are bound to feel the strain.
Discover how hooded and non hooded eyelids can impact your eye appearance. Find out the key difference between both of them in our Hooded vs Non Hooded Eyelids comprehensive guide.
Effects of Eye Strain

Understanding how long eye strain lasts requires us first to grasp its effects:
Temporary Vision Issues
After a long day in front of a screen, your vision gets a little blurry. This is a temporary effect of eye strain and usually resolves after giving your eyes a rest.
Headaches
Continuous focus without breaks can lead to tension headaches. These headaches typically feel like a tight band around your forehead.
Sleep Disruptions
Excessive exposure to blue light, especially in the evening, can disrupt the production of melatonin, a hormone responsible for regulating sleep. This can lead to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Chronic Discomfort
If not addressed, recurrent eye strain can lead to chronic discomfort, making daily activities challenging and reducing overall productivity.
Symptoms of Eye Strain

Eye strain, or asthenopia, can manifest in various symptoms. When our eyes get tired from intense use, such as reading in poor light or staring at a digital screen for extended periods, they can exhibit the following signs:
Blurred Vision
The clarity of sight can become compromised, causing objects and text to appear fuzzy or out of focus.
Double Vision
This involves seeing two images of a single object, either side by side or one above the other.
Red or Dry Eyes
The eyes can become red due to irritation, and there might be a feeling of dryness or a gritty sensation in the eyes.
Headaches

These can be felt around the temple area, forehead, or even the back of the head. Eye strain-related headaches often feel like a tightening sensation around the head.
Sore or Tired Eyes
A general feeling of discomfort or fatigue in the eyes is often described as a heavy or burning sensation.
Increased Sensitivity to Light
One might find bright lights or even normal room lighting to be harsh or glaring.
Dark Circles Under the Eyes
Prolonged eye strain and fatigue can sometimes lead to the appearance of dark circles.
Find out more symptoms related to different types of eye care problems on any of the healthcare blogs in USA.
Tips to reduce eye strain

Reducing eye strain is essential for maintaining good eye health, especially in our increasingly digital world. Here are some tips to help alleviate and prevent it:
Follow the 20-20-20 Rule
Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and focus on something at least 20 feet away. This simple exercise can significantly reduce it from prolonged work.
Use Computer Glasses
These are specifically designed for the distance between your eyes and the computer screen, reducing the effort your eyes need to focus. They may also have a tint or coating that reduces blue light exposure.
Adjust Screen Brightness and Contrast

Ensure that the brightness of your screen matches the lighting in your room. It shouldn’t be too bright or too dark.
Enlarge Text Size
In case you spend too much time sitting in front of a computer screen, you should Increase the font size on your devices to prevent squinting.
Reduce Glare
Use anti-glare screens or protective eyewear. Adjust the screen angle to minimize reflections from windows and lighting.
Blink Regularly
Blinking moistens the eyes, reducing dryness and discomfort. Remind yourself to blink more often, especially when using digital devices.
Maintain Proper Screen Distance
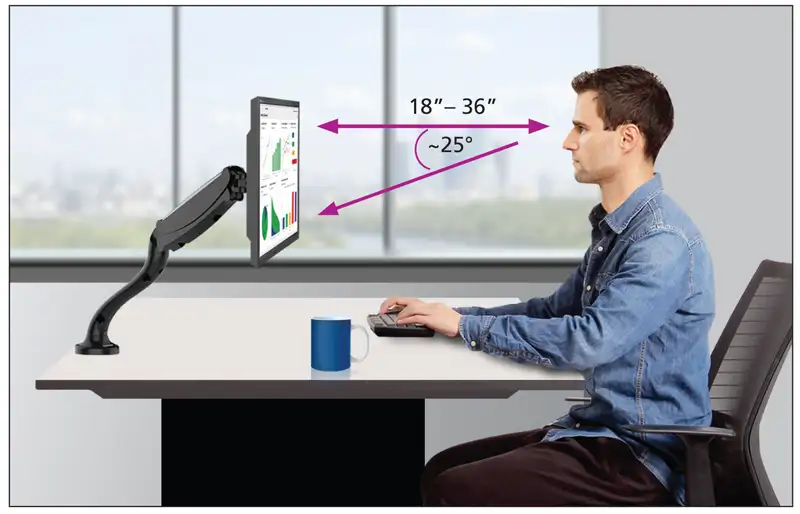
The screen should be about an arm’s length away. The top of the screen should be at or just below eye level.
Adjust Lighting
Use indirect lighting to avoid glare and extreme brightness. Position your primary light source behind you and direct it onto your task, not into your eyes.
Curious about the transformative effects of Botox on your eyes? Dive into our comprehensive guide on Botox Before and After Eyes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question “How long does eye strain last?” can have varied answers based on individual habits and underlying causes. However, with proper eye care practices, such as the 20-20-20 Rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds), using proper lighting, and ensuring regular eye check-ups, it can be effectively managed.
FAQs
How long does it take for eyes to heal from strain?
Typically, eyes recover from strain after a few hours of rest. However, persistent symptoms may require a day or two of reduced visual tasks. If symptoms continue, it’s advisable to consult an eye specialist.
Can eye strain last for 3 days?
Yes, eye strain can last for 3 days, especially if the contributing factors continue or aren’t addressed. However, if symptoms persist beyond this period, it’s important to consult an eye specialist.
How long does digital eye strain last?
Digital eye strain symptoms typically subside after a few hours once you take a break from screens. However, if the exposure continues or habits remain unchanged, symptoms can persist.
How do strained eyes feel like?
Strained eyes often feel tired, sore, or uncomfortable. Symptoms can include blurred vision, headaches, sensitivity to light, dry or watery eyes, and a feeling of heaviness or difficulty in keeping the eyes open. There might also be an urge to rub the eyes frequently.
Do I need glasses for eye strain?
Not always. Eye strain can result from various causes, including prolonged screen use, improper lighting, or fatigue. However, if it persists or if you experience other vision problems like blurred or double vision, it might indicate a refractive error. In such cases, glasses or updated prescription lenses can help.